Disease Review
Organophosphate - Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine Manual 8th Ed.
1. Absorption
ingestion, inhalation (e.g., nerve gas agents), and dermal routes.
2. Toxicity
binding and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, causing excess accumulation of acetylcholine and stimulation of cholinergic receptors, of both the muscarinic and nicotinic receptor types.
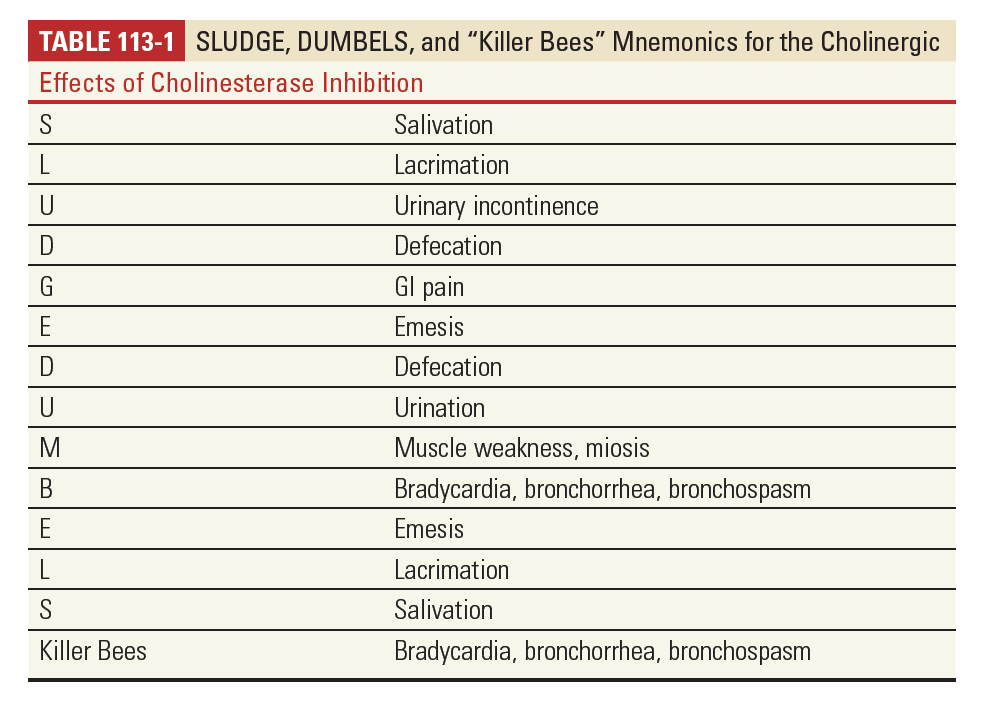
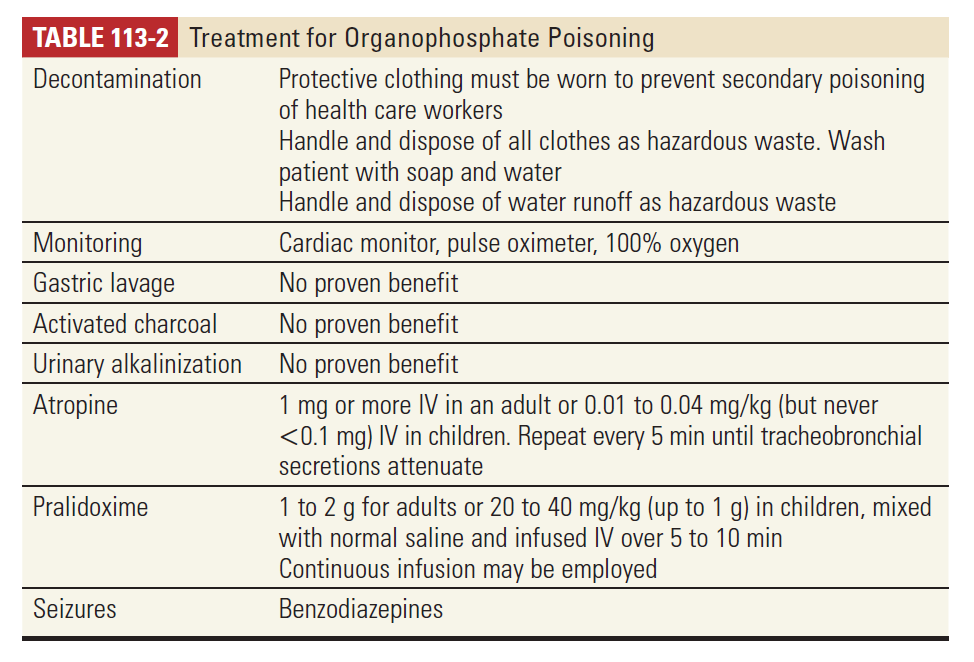
3. Treatment
1) 100% oxygen and focus on airway management
Nondepolarizing agents should be used for rapid sequence intubation.
Succinylcholine(metabolized by plasma cholinesterase) may result in prolonged paralysis.
2) Large amounts of Atropine : key treatment
Tachycardia and dilated pupils are not contraindications to additional atropine.
Atropine will only reverse the muscarinic effects, but not the nicotinic effects of excess acetylcholine.
Glycopyrrolate or high-dose diphenhydramine can be substituted for atropine if it is not available.
3) Minimal exposures
6 to 8 hours of observation. Significant poisonings require intensive care monitoring.
에피소드 내용












































































































































































